EMI Suppression Capacitor
EMI suppression capacitors, specifically X and Y capacitors, play a critical role in filtering noise and preventing electromagnetic interference from propagating through the AC mains input.
These are safety-rated capacitors specifically designed to suppress conducted EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) in power lines.
They are placed at the input stage of AC-powered devices to:
- Filter out high-frequency noise from entering or leaving the equipment.
- Provide isolation and safety during fault conditions like surges or insulation breakdown.
- Maintain EMC compliance with regulatory bodies (like FCC, CISPR, etc.).
Safety Classes: X and Y Capacitors
These capacitors are categorized based on where they're connected and the safety risks involved:
X Capacitors:
X capacitors are typically made from metallized polypropylene film and Encapsulated in flame-retardant epoxy. They are designed to withstand repetitive voltage surges (due to lightning, switching, etc.). They have internal self-healing properties: a breakdown in the dielectric causes local vaporization of metal to isolate the fault.
They...
- Connected between Line (L) and Neutral (N).
- Used to suppress differential-mode noise (current flows in opposite directions in the two conductors).
- Typically value (e.g. 0.1 µF – 1 µF).
- Not safety-critical, but still need to withstand surges/spikes.
Safety Classes:
X1
Surge withstand ⇒ 2.5kV to 4kV
Application ⇒ Industrial, Long cables etc.
X2
Surge withstand ⇒ 1.2kV to 2.5kV
Application ⇒ Consumer Electronics
X3
Surge withstand ⇒ <1.2kV
Application ⇒ Benign Environment
Y Capacitors
Y capacitors are typically film-type, but with double insulation and larger creepage distances. They are constructed for reinforced insulation between live and grounded parts. They use ceramic dielectric (Class 1 or 2) with strict control over breakdown and leakage.
They...
- Connected from Line or Neutral to Earth Ground.
- Suppress common-mode noise (same noise on both Line and Neutral).
- Typically much smaller (e.g. 470 pF – 4700 pF).
- Safety-critical: a short or failure here can result in current leakage to chassis or human-accessible parts.
Safety Classes:
Y1
Surge withstand ⇒ 5kV to 8kV
Application ⇒ Industrial, Long cables etc.
Y2
Surge withstand ⇒ 2.5kV to 5kV
Application ⇒ Consumer Electronics
Y3
Surge withstand ⇒ <2.5kV
Application ⇒ Benign Environment
Y-caps must pass rigorous safety standards to ensure fail-safe behavior — if they fail, they must fail open (not short).
A short here can result in current leakage to chassis or human-accessible parts.
Circuit Configuration in Practice
In a typical EMI input filter

- X cap sits across L and N — suppresses differential-mode noise.
- Y caps connect L and N individually to GND — suppress common-mode noise.
- Often combined with common-mode chokes and ferrites for enhanced performance.
Design Considerations
1. Capacitance vs. Leakage Current
- Y capacitors create a small leakage path to ground. Too much capacitance = excessive leakage.
- Most standards limit leakage current to < 0.5–1 mA.
2. Creepage and Clearance
- Since Y capacitors bridge line/neutral to ground, PCB layout must follow isolation rules for safety (e.g., >6.4 mm creepage for reinforced insulation).
3. Filter Design Integration
- Y cap sholud be placed after the common mode choke
- X and Y caps should be used with self-healing film dielectric (typically metallized polypropylene).
4. Regulatory Compliance
Must comply with standards like:
- IEC 60384-14 (for safety-rated capacitors)
- UL/EN 60950 / 62368 (product safety)
Typical Cap Values
X-Cap ⇒ 0.1 µF to 1 µF
Typical voltage rating: 250 to 310VAC
Y-Cap ⇒ 470 pF to 4700 pF
Typical voltage rating: 250 to 500VAC
Selection Guidelines
For X Capacitor:
- Capacitance: Balance EMI suppression vs. inrush energy
- Choose X2 for consumer; X1 for industrial/high-surge lines
- Ensure flame-retardant housing (UL 94 V-0)
For Y Capacitor:
- Choose smallest capacitance that gives adequate common-mode filtering
- Watch leakage current budget
- For medical/portable devices: ≤ 0.1 µF total Y-cap (often < 2x 2200 pF)
- Look for Y1 in harsh environments or reinforced insulation designs
Example: AC Input Filter of a Laptop Adapter
- X Capacitor: 0.1 µF 275V AC (Class X2)
- Y Capacitors: 2 × 2200 pF 250V AC (Class Y2) from L/N to chassis ground
- Total leakage current: ~0.3 mA at 60Hz — safe and compliant
Applications
- SMPS (Switched-Mode Power Supplies)
- AC adapters and chargers
- LED drivers
- Home appliances
- Industrial controllers
Common-Mode vs. Differential-Mode Noise
Electrical Noise
Electrical noise is any unwanted signal superimposed on a desired electrical signal that can distort, interfere, or reduce signal fidelity. In high-speed circuits and EMC analysis, this noise is typically classified as:
-
Differential-Mode (DM) Noise
-
Common-Mode (CM) Noise
These two have different origins, transmission paths, and countermeasures.
1. Differential-Mode Noise – “Normal-mode noise”
Differential-mode noise is the voltage difference between two conductors of a signal or power line. It represents the intentional signal path where the noise rides in opposition across the two conductors.
Current Flow:
The noise flows in opposite directions in a loop between the two wires. If one conductor has a +5V spike and the other has -5V, the differential noise is 10V.
Example Use Cases:
-
Power rails: +V and GND in DC systems
-
Communication: USB, HDMI, Ethernet pairs
-
Analog signals: Sensor lines in instrumentation
Typical Sources:
-
Switch-mode power supplies (SMPS) – due to rapid switching
-
High-speed data lines – signal reflections, ringing
-
Magnetic coupling – between traces or cables
-
Load changes – from motors, solenoids, or relays
Mitigation Strategies:
-
Differential-mode filters: Series inductors with capacitors across lines
-
Matched impedance design: Prevents signal reflection and ringing
-
Twisted pairs: Cables twisted to cancel out opposing fields
-
Short trace lengths: Reduces antenna effect
2. Common-Mode Noise – “Ground-referenced noise”
Common-mode noise appears equally and in phase on both conductors relative to a common reference point, usually system ground or chassis.
Current Flow:
Both wires carry the noise in the same direction, and the return path flows through the ground plane, earth, or shielding.
Real-World Example:
-
Long USB cables pick up RF noise equally on both data lines.
-
AC power lines exposed to EMI from nearby radio towers or industrial machines.
Typical Sources:
-
Electrostatic coupling: From nearby high-voltage lines
-
Radiated emissions: Antenna-like behavior of cables or traces
-
Ground potential differences: Between system components (e.g., USB ground loop)
-
Parasitic capacitance: Between PCB traces and the chassis
Mitigation Strategies:
-
Common-mode chokes: High impedance to CM signals, low to DM signals
-
Shielded cables and connectors: With 360° termination to chassis
-
Isolated grounds: Breaks in ground loops
-
Ferrite beads/clamps: On external cables
3. Visualizing the Current Paths
Noise Type: Differential Mode
Current Direction: Opposite directions on each line, Reference Point: Across the pair, Return Path: One conductor to another
Noise Type: Common Mode
Current Direction: Same direction on both lines, Reference Point: Ground or chassis, Return Path: Through system or earth ground

4. Importance in EMC Testing
Emissions:
-
Differential-mode emissions are mostly conducted (via power/signal lines).
-
Common-mode emissions often become radiated, as CM currents form large loop areas (acting like antennas).
Compliance Implications:
-
Regulatory bodies (e.g., FCC, CISPR, IEC) test both emission types.
-
CISPR 22/32 and FCC Part 15 focus heavily on common-mode conducted emissions in lower frequency bands (150 kHz–30 MHz).
5. Filtering Techniques Comparison
Filter Type: CM Filter
Effective Against: Common-mode noise, Components Used: Common-mode choke, Y-capacitors
Filter Type: DM Filter
Effective Against: Differential-mode noise, Components Used: Series inductors, X-capacitors
Notes:
-
Y-capacitors connect from line to ground (handle CM).
-
X-capacitors go across the line pair (handle DM).
6. Example: SMPS Input Filtering
In a switch-mode power supply, both noise types are generated:
-
Differential noise arises from the switching node oscillations.
-
Common-mode noise results from parasitic capacitance between high-frequency switching nodes and the chassis.
The input filter typically includes:
-
X-capacitor across line and neutral (DM)
-
Y-capacitors from line/neutral to ground (CM)
-
Common-mode choke for both conductors
7. Application-Specific Impacts
High-Speed Digital Systems:
-
Differential signaling (LVDS, HDMI, USB) relies on clean DM paths. Noise degrades data integrity (eye diagrams, jitter).
-
CM noise can cause cross-talk between pairs or fail EMC radiated tests.
Automotive:
-
CM noise is a major concern due to long wire harnesses acting as antennas.
-
Standards like ISO 11452 and CISPR 25 require thorough CM filtering.
Medical Devices:
-
Safety and immunity to external EMI are critical—isolation transformers, CM chokes, and filtering are used to ensure patient safety and compliance (e.g., IEC 60601-1-2).
Conclusion
|
Aspect |
Differential-Mode Noise |
Common-Mode Noise |
| Flow Direction | Opposite on conductors | Same on both conductors |
| Reference | Between lines | Against ground or chassis |
| Typical Source | Internal circuit switching | External EMI, parasitic coupling |
| Testing Concern | Conducted emissions | Radiated + conducted emissions |
| Mitigation | X-caps, twisted pairs, impedance match | CM chokes, Y-caps, shielding |
Both types of noise must be addressed for:
-
Regulatory compliance
-
Signal integrity
-
Functional reliability
Designers should always measure both types during EMC testing and implement layered filtering and shielding strategies.
Common Mode Chokes for EMI Suppression
Introduction to Common Mode Noise
Common mode noise refers to the interference that appears in phase and with equal amplitude on both lines of a differential signal or a power line with respect to a common reference (typically ground). It’s a major source of EMI because it can easily radiate from cables or PCB traces, especially when long conductors act as antennas.
Common Mode Chokes
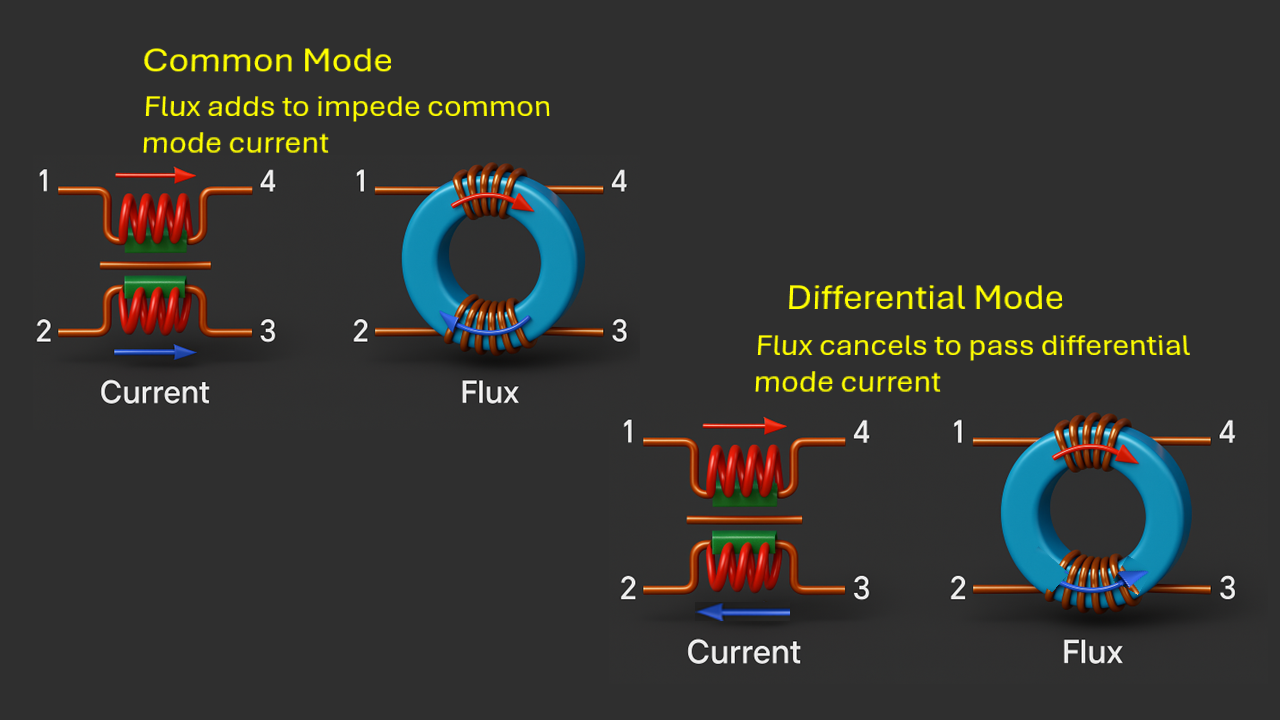
A common mode choke (CMC) is a type of passive filter made by winding two or more conductors (typically for a differential signal) on a magnetic core in such a way that:
Differential signals pass unaffected.
Common mode signals (noise present equally on both lines) induce magnetic flux in the same direction, which creates impedance and attenuates the noise.

Structure and Working Principle
A common mode choke is essentially a toroidal or cylindrical magnetic core (often ferrite or powdered iron) with two windings of wire wound around it—usually side by side or bifilar wound.
Key components:
- Magnetic Core:
- Typically ferrite material with high permeability.
- Acts as the medium for magnetic flux.
- Windings (Coils):
- Two insulated copper wires are wound around the core.
- The wires carry current for the differential signal (i.e., one wire for signal, one for return).
- Pins / Terminals:
- The choke is mounted on a PCB, with four pins—two for each coil end.
Working Principle of a Common Mode Choke
The common mode choke blocks common mode currents (noise or interference that flows in the same direction on both lines) but allows differential mode currents (normal signal current that flows in opposite directions) to pass freely.
Here’s how it works:
- For differential mode currents:
- Current flows in opposite directions in the two windings.
- Their magnetic fields cancel each other out in the core.
- Result: Minimal inductance → signal passes through with little impedance.
- For common mode currents (e.g., EMI or RF noise):
- Current flows in the same direction through both windings.
- Their magnetic fields add up, reinforcing the magnetic flux in the core.
- Result: High inductance → blocks or attenuates noise effectively.
Think of a CMC as a filter that says:
- "If the currents are opposite (real signal), I’ll let them through with no problem."
- "If the currents are the same (noise), I’ll choke them with high impedance."
Applications in PCB and System Design
Power lines: To suppress switching noise from DC-DC converters.
USB, HDMI, Ethernet: To block radiated and conducted emissions from high-speed I/O.
CAN/LIN buses: To reduce susceptibility and emissions in automotive networks.
Audio circuits: To remove hum and external noise from cables.
Design Considerations for Common Mode Chokes in EMI Suppression
Effective use of common mode chokes (CMCs) requires thoughtful integration into PCB and system-level designs. The following key design considerations ensure optimal EMI mitigation without compromising signal integrity or power delivery.
Common mode chokes (CMCs) are vital components in suppressing electromagnetic interference (EMI), particularly common mode noise that tends to couple onto cables and radiate from electronic systems. To achieve optimal performance, careful attention must be paid to several design factors that influence both EMI suppression and signal integrity.
1 Frequency Characteristics and Impedance Profile
The effectiveness of a CMC is highly dependent on its impedance profile across frequency. An ideal CMC offers high impedance to common mode noise while remaining transparent to differential mode signals. Design selection should be guided by the spectral content of the unwanted emissions. In most digital systems, common mode noise appears predominantly in the 10 MHz to 1 GHz range. Therefore, chokes must be selected based on insertion loss data provided by the manufacturer, ensuring that they provide sufficient attenuation in this band.
Example: In USB 2.0 applications, significant emissions occur between 30 MHz and 300 MHz. A CMC designed to provide high impedance within this band will help in meeting EMI compliance requirements such as CISPR 32 or FCC Part 15.
2 Current and Voltage Handling Capability
Another critical consideration is the current-carrying capability of the CMC. The selected choke must support the continuous operating current of the line without causing magnetic saturation of the core. Saturation significantly reduces the common mode impedance and thereby degrades EMI suppression performance. Additionally, the choke’s voltage rating must exceed the peak differential voltage on the line to prevent insulation failure or dielectric breakdown between windings.
3 Differential Mode Transparency
While the primary purpose of a CMC is to suppress common mode noise, it is equally important to ensure that differential mode signals are not attenuated or distorted. This is particularly relevant for high-speed data lines such as USB 3.0, HDMI, or Ethernet, where signal integrity is paramount. In such applications, low differential impedance and symmetrical winding structures are essential to minimize skew and avoid signal degradation.
4 Optimal Placement Strategy
The physical placement of the CMC on the PCB significantly impacts its effectiveness. It should be placed as close as possible to either the source of EMI (e.g., switching regulators) or the I/O connectors (e.g., USB or RJ45 jacks). This minimizes the path length through which common mode currents can radiate. In systems with well-defined subsystem boundaries, placing the choke at the interface helps isolate noise between domains.
5 PCB Layout Guidelines
Proper PCB layout is essential to maintain the effectiveness of the CMC. The traces connected to the choke must be routed symmetrically to preserve differential balance. Any mismatch can lead to mode conversion, wherein differential signals generate additional common mode noise. The loop area between the signal paths and their return currents should be minimized to reduce parasitic inductance. Moreover, ground stitching vias should be included near the choke to provide a low-impedance return path for high-frequency currents.
6 Core Material and Winding Structure
The core material plays a crucial role in determining the frequency response of the choke. Ferrite materials are widely used due to their high permeability and frequency-selective damping properties. The winding structure, especially bifilar winding, enhances common mode suppression by ensuring tight magnetic coupling while allowing differential signals to pass with minimal interference.
7 Thermal and Mechanical Considerations
As passive components, CMCs also dissipate heat due to core losses and copper resistance. Therefore, they should be selected with a current derating margin to account for ambient temperature, self-heating, and aging effects. The choice between surface-mount and through-hole packages depends on current requirements, thermal dissipation, and mechanical robustness. Surface-mount components are preferred for compact designs and automated assembly processes.
8 Multi-Channel and System-Level Integration
In systems with multiple parallel data lines (e.g., differential pairs in HDMI or Ethernet), multi-channel CMCs can reduce board space and ensure uniform filtering across all lines. However, inter-channel crosstalk and imbalance must be considered during layout and simulation. Additionally, CMCs should be included as part of a comprehensive EMI strategy, integrated with other filtering elements such as ferrite beads and LC filters.
9 EMC Compliance and Validation
Ultimately, the choice and integration of CMCs must be validated through EMI pre-compliance and compliance testing. Techniques such as Line Impedance Stabilization Network (LISN) measurements, spectrum analysis, and near-field probing help assess the effectiveness of common mode suppression. Iterative tuning of choke parameters and placement is often required to meet stringent regulatory limits.
Comparison with Other Filters
|
Filter Type |
Best For |
Blocks |
Notes |
|
Common Moe choke |
Common Mode EMI |
Common mode Noise |
Transparent to differential signals |
|
Ferrite Bead |
Broadband Suppression |
High Frequency Noise |
Acts as lossy inductors |
|
LC Filter |
Specific frequency range |
Both Common and differential Noise |
Requires careful tuning |
Example
Consider a USB 3.0 line:
Without a CMC: Common mode currents induced by fast switching can radiate via the cable, failing EMI tests.
With a CMC: Noise is attenuated before reaching the cable, ensuring compliance with standards like CISPR 32.
Automotive Pulses
Automotive pulses refer to specific transient voltage waveforms that occur in a vehicle's electrical system. These pulses are defined by standards (like ISO 7637, SAE J1113, or LV 124) and used primarily for EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) testing of automotive electronic components and systems.
These tests simulate real-world disturbances (like load dumps, switching transients, inductive kicks) to ensure components can survive and operate correctly in harsh automotive environments.
Modern vehicles contain many ECUs, sensors, and actuators. They're exposed to:
- Alternator spikes
- Battery disconnection
- Relay switching
- Ignition transients
- Electrostatic discharge (ESD)
To ensure reliable operation, these pulses are simulated and tested in labs.
Pulses as per ISO 7637-2
ISO 7637-2 (for 12V and 24V systems)
The most widely used for electrical transients on supply lines.
|
Pulse |
Description |
Typical Cause |
|
Pulse 1 |
Negative spike |
Battery disconnect while inductive loads are ON |
|
Pulse 2a/2b |
Positive/negative spikes |
Switching of inductive loads |
|
Pulse 3a/3b |
Fast transients |
Arising from relay contact bounce |
|
Pulse 4 |
Voltage drop |
Engine cranking |
|
Pulse 5 |
Load dump |
Battery disconnect while alternator is charging |
Pulse Characteristics (ISO 7637-2)
Pulse 1
- Negative Spike
- Cause: Battery disconnection from Inductive Loads (motor, Solenoid)
- Affect: Power supply circuit, Microcontroller

| Parameters | Nominal 12 V system | Nominal 24 V system |
| Us | −75 V to −150 V | −300 V to −600 V |
| Ri | 10 Ω | 50 Ω |
| td | 2 ms | 1 ms |
| tr | 1 μs | 3 μs |
| t1 | ≥0.5 s | |
| t2 | 200 ms | |
| t3 | <100 μs | |
Pulse 2a
- Positive Spike
- Cause: Sudden interruption of current due to sudden disconnection of large loads
- Affect: Voltage regulators and semiconductors devices

| Parameters | Nominal 12V & 24V system |
| Us | +37 V to +112 V |
| Ri | 2 Ω |
| td | 0.05 ms |
| tr | 1 μs |
| t1 | 0.2 s to 5 s |
Pulse 2b
- Negative Spike
- Cause: Alternator field decay, Alternator’s field winding de-energises after engine shutdown
- Affect: ECU Reset

| Parameters | Nominal 12 V system | Nominal 24 V system |
| Us | 10 V | 20 V |
| Ri | 0 Ω to 0.05 Ω | |
| td | 0.2 s to 2 s | |
| tr | 1 ms | |
| t12 | 1 ms | |
| t6 | 1 ms | |
Pulse 3a
- Fast Transients – Negative
- Cause: Relay chatter (very fast edge), switching processes. Characteristics of these transients are influenced by distributed capacitance and inductance of the wiring harness.
- Affect: Signal Interference and component malfunction

| Parameters | Nominal 12 V system | Nominal 24 V system |
| Us | −112 V to −220 V | −150 V to −300 V |
| Ri | 50 Ω | |
| td | 150 ns ± 45 ns | |
| tr | 5 ns ± 1.5 ns | |
| t1 | 100 μs | |
| t4 | 10 ms | |
| t5 | 90 ms | |
Pulse 3b
- Fast Transients – Positive
- Cause: Relay chatter (very fast edge), switching processes. Characteristics of these transients are influenced by distributed capacitance and inductance of the wiring harness.
- Affect: Sensors and controllers

| Parameters | Nominal 12 V system | Nominal 24 V system | |
| Us | +75 V to +150 V | +150 V to +300 V | |
| Ri | 50 Ω | ||
| td | 150 ns ± 45 ns | ||
| tr | 5 ns ± 1.5 ns | ||
| t1 | 100 μs | ||
| t4 | 10 ms | ||
| t5 | 90 ms | ||
Pulse 4
- Cranking Pulse - Slow Negative
- Cause: Supply voltage reduction caused by energising starter motor of internal combustion engine.
- Affect: Sensors and controllers

| Parameters | Nominal 12 V system | Nominal 24 V system |
| Us | − 6V to − 7V | − 12V to − 16V |
| Ua | − 2.5V to − 6V with |Ua| ≤ |Us| | − 5V to − 12V with |Ua| ≤ |Us| |
| Ri | 0 Ω to 0.02 Ω | |
| t7 | 15 ms to 40 ms | 50 ms to 100 ms |
| t8 | ≤ 50ms | |
| t9 | 0.5 s to 20 s | |
| t10 | 5ms | 10ms |
| t11 | 5ms to 100ms | 10ms to 100ms |
Pulse 5a – Load Dump
- Unsuppressed Alternator Surge- Without Protection
- In the event of a discharged battery being disconnected while the alternator is generating charging current and with other loads remaining on the alternator circuit at this moment.
- Affect: ECU, Sensor, Power circuit
| Parameters | Nominal 12 V system | Nominal 24 V system |
| Us | 65V to 87V | 123V to 174V |
| Ri | 0.5 Ω to 4 Ω | 1 Ω to 8 Ω |
| td | 40ms to 400ms | 100ms to 350ms |
| tr | 10ms | |
Pulse 5b – Load Dump
- Suppressed Alternator Surge- with protection (like Zener diode, TVS diode)
- In the event of a discharged battery being disconnected while the alternator is generating charging current and with other loads remaining on the alternator circuit at this moment.
- Affect: ECU, Sensor, Power circuit

| Parameters | Nominal 12 V system | Nominal 24 V system |
| Us | 65V to 87V | 123V to 174V |
| Us* | As specified by manufacturer | |
| td | 40ms to 400ms | 100ms to 350ms |
Testing Setup
Usually tested in the lab using an EMC test bench with:
- Pulse generators
- Coupling/decoupling networks
- Oscilloscopes
- Electronic loads or real DUTs
The DUT (Device Under Test) must withstand or operate normally depending on the pulse.
Other Standards
- SAE J1113 – Similar to ISO 7637, North American usage
- LV 124 / LV 148 – German standards for 12V/48V systems (used by BMW, VW, Daimler, etc.)
- ISO 16750-2 – Broader set including electrical load, jump start, reverse polarity, etc.


